Chameleon disease is often called osteochondrosis of the chest. It is quite difficult to diagnose, it is often confused with other diseases. At the same time, osteochondrosis rarely occurs in the thoracic region and is a lesion of the intervertebral discs.
How does the disease occur?
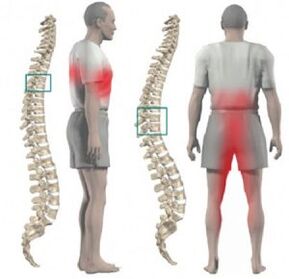
Osteochondrosis affecting the chest is often disguised as a pathology of internal organs. It manifests itself with pain in the heart, shortness of breath, a feeling of lack of air when inhaling, panic attacks. Therefore, the diagnosis of thoracic osteochondrosis is somewhat difficult.
The intervertebral discs of each spine consist of the nucleus pulposus and the stronger annulus fibrosus. The latter protects the semi-liquid core and protects it from injury.
But due to certain reasons there are situations where metabolic processes slow down and as a result there is increased pressure on the discs. In this case, the disk is deformed, its structure is disturbed.
If treatment is not started at this stage, the symptoms become even more pronounced. The annulus fibrosus may crack and the nucleus dry out.
The disease leads to damage to spinal nerves, destruction of joints.
Causes of the disease
Various reasons can provoke the appearance of osteochondrosis in the chest area, the most common among them are:
- chest trauma;
- inactivity, sedentary work (applies to those who work on a computer or are drivers);
- scoliosis.
In addition, problems with the chest region are related to its structure. There are many more crammed discs in this space of the spine than in the lower back or cervical region. Due to the presence of ribs and a muscular corset, the chest area moves less.
There are cases when the main cause of osteochondrosis in the thoracic region of the spine is osteochondrosis of other departments.
What is the danger of osteochondrosis?
If, despite the symptoms, treatment is delayed, osteochondrosis in the chest area can lead to a number of complications and problems, including:
- intercostal neurology - when the intercostal nerves are compressed;
- spinal cord compression;
- shortness of breath, heart problems;
- problems with the functioning of the intestines, liver, kidneys;
- problems with the chair;
- hernia.
What diseases can be confused with osteochondrosis?
As mentioned above, the symptoms of osteochondrosis do not always allow a diagnosis to be quickly established. That is why osteochondrosis of the chest can be accidentally confused with:
- pathologies of the mammary glands;
- diseases of the digestive system;
- pneumonia (two diseases can be distinguished by a dry cough, shortness of breath and fever with pneumonia. In the case of osteochondrosis, such symptoms are not observed);
- heart attack (in this case, osteochondrosis can be distinguished by a cardiogram);
- renal colic.
Symptoms
With osteochondrosis of the chest, symptoms of radiculopathy most often appear, i. e. associated with compression of the nerve trunks and the appearance of herniation between the vertebrae. In this case, severe pain occurs after physical work, training. Symptoms in the following weeks become more pronounced depending on the location of the hernia. If in the upper part, then the liver, heart, stomach suffer. If it is lower, then the problems are related to the kidneys.

The location of the hernia also has a significant impact on symptoms. So, if it is located closer to the middle, the pains become stronger, last for several weeks continuously and do not decrease after taking medication. Lateral hernia manifests itself with periodic and mild pain, local loss of sensitivity is possible.
Osteochondrosis of the chest, which is accompanied by compression of the spinal cord, has the following symptoms:
- strong pain;
- numbness of the limbs;
- pain radiates to the stomach, groin, legs;
- pelvic organ dysfunction.
In addition to the above, osteochondrosis can manifest additional symptoms, in particular:
- numbness of individual skin areas;
- sensation of "goosebumps" in the chest;
- nail brittleness;
- dry skin, peeling;
- disorders of the gastrointestinal tract (diarrhea or, conversely, constipation);
- throatache;
- itching or feeling cold in the lower extremities.
Dorsago as a consequence of osteochondrosis of the thoracic region
Osteochondrosis in the chest is characterized by the presence of dorsago. This is one of its main symptoms. In fact, the word "dorsago" should be understood as a very strong and sudden pain in the chest. It is often called "shooting" because the sensations in this case are the same as in a stab wound. A severe attack of dorsago makes breathing difficult and makes free movement impossible. This happens after prolonged physical exertion in people who already suffer from osteochondrosis and joint diseases.
Weak but increasing and prolonged pain in the chest area is called dorsalgia. More pronounced symptoms when a person bends over. The pain can also increase at night, especially often this happens in women suffering from osteochondrosis who wear shoes with heels.
Diagnosis
For thoracic osteochondrosis, effective treatment should be carried out. Symptoms without it will only intensify and interfere with normal life.
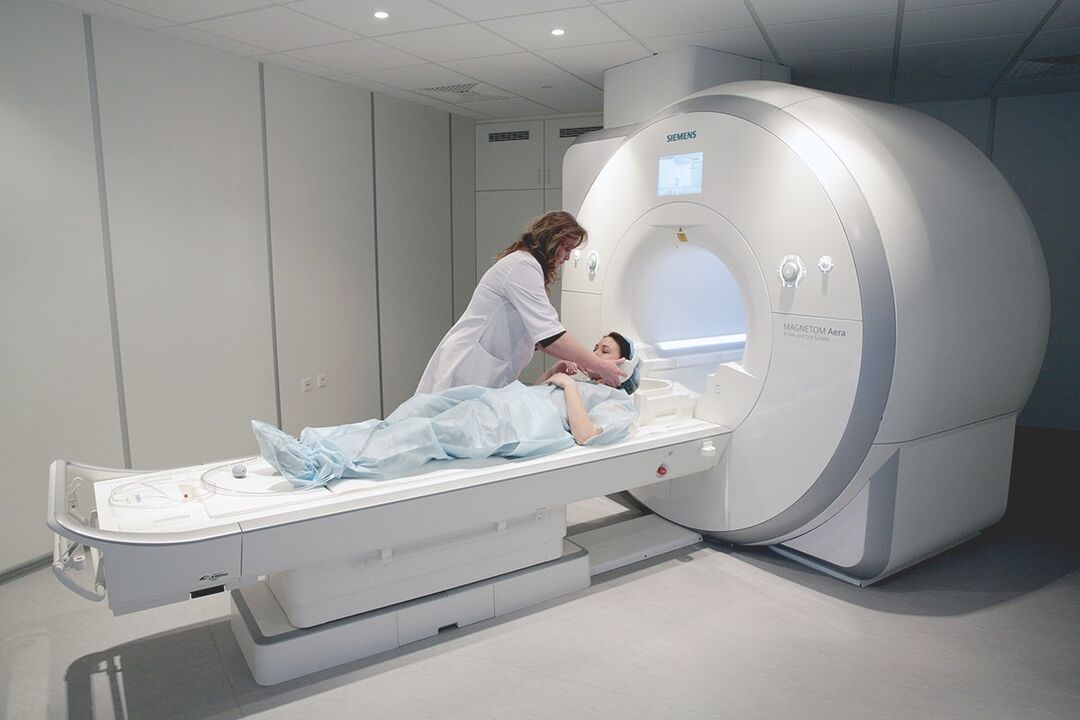
After detecting the symptoms, the doctor refers the patient for further examination. Among the methods of diagnosis that are most often used for osteochondrosis of the chest are:
- MRI. The tomograph makes it possible to obtain a clear three-dimensional image with contrast of the examined area of the human body. Because of this, the doctor can see the condition of the vertebrae of the chest, assess the health of the joints. The procedure does not take much time (from 20 to 55 minutes) and is painless. The patient should expose the chest and lie down on a special couch. The scanner, which is placed on the person, then takes a picture of the sections.
- Ultrasound procedure. Before carrying out treatment, it is worth making sure that osteochondrosis of the chest is not accompanied by tumors. An ultrasonic method is suitable for this. The device clearly shows the condition of soft tissues, joints, intervertebral discs. As in the first case, the procedure does not take much time and is painless. With the help of ultrasound, the chest area of pregnant women and even children can be examined.
Of course, the doctor does not offer treatment until the patient passes the general clinical tests of blood and urine, as well as the results of the electrocardiogram. The latter allows the doctor with similar symptoms to distinguish thoracic osteochondrosis from a heart attack or other heart problems.
Treatment
Turning to a neuropathologist, a patient with thoracic osteochondrosis will receive a recommended course of treatment. The methods and drugs, as well as the duration of their use, are determined by the doctor in each individual case. As a rule, when osteochondrosis is detected in the chest, doctors recommend:
- drug treatment - its purpose is to relieve pain, muscle spasms, reduce the inflammatory process, restore the tissues around the joints and vertebrae;
- physiotherapy - aims to use ultrasound waves, electric current or laser to relieve acute pain in the chest area and reduce the negative effects of osteochondrosis, provides treatment of joints;
- manual therapy - thanks to the massage movements of a specialist, it is possible to align the position of the discs of the chest region, to relieve the spasm;
- isometric kinesitherapy (gymnastic treatment) - helps to improve the mobility of the chest area, relieves pain.
In addition to the methods described above, the treatment of osteochondrosis can be carried out using hirudotherapy, millimeter wave therapy, apitherapy, magnetotherapy and other methods.



















